Introduction to Homesteading
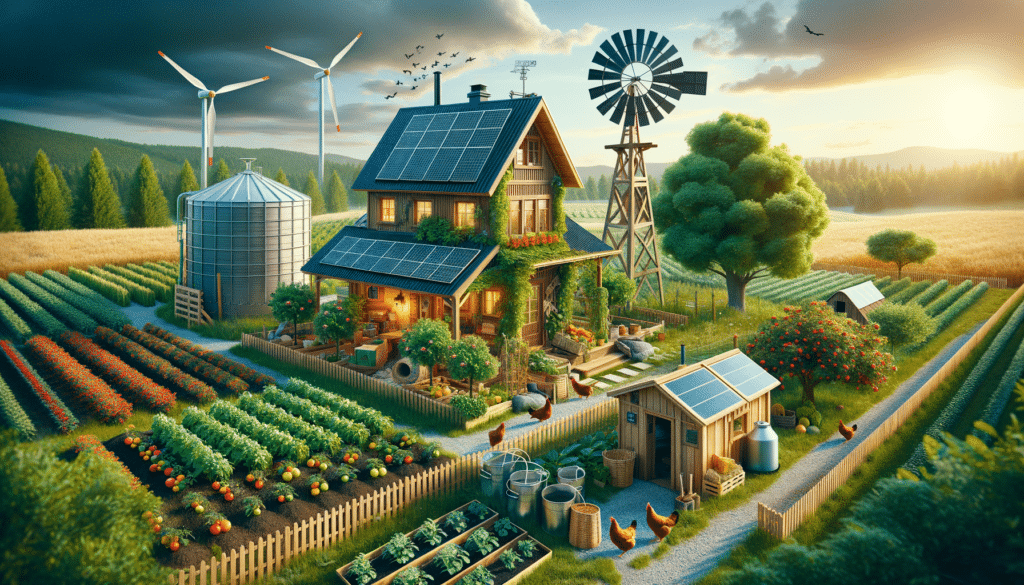
Homesteading, a lifestyle dedicated to self-sufficiency, has become increasingly relevant in today’s world. As people seek to reduce their carbon footprint and embrace sustainable living, homesteading offers a viable path. It involves growing your own food, generating your own energy, and often, living off the grid. While it may seem daunting, homesteading is a rewarding journey that reconnects individuals with nature and their own resourcefulness.
The Foundations of Homesteading
At its core, homesteading is about creating a sustainable and self-reliant lifestyle. This involves several key components:
- Food Production: Growing your own fruits, vegetables, and herbs is a cornerstone of homesteading. Many homesteaders also raise livestock for eggs, milk, and meat.
- Energy Independence: Utilizing renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind power, helps homesteaders reduce reliance on external energy suppliers.
- Water Management: Collecting rainwater and maintaining a sustainable water supply are crucial for a successful homestead.
- Waste Reduction: Composting and recycling reduce waste and contribute to a closed-loop system.
These elements work together to create a lifestyle that is not only environmentally friendly but also economically viable. Homesteaders often find that their initial investments in infrastructure pay off over time as they reduce their dependency on external resources.
Homesteading Techniques and Practices
Homesteading involves a variety of techniques and practices that contribute to a sustainable lifestyle. Some popular methods include:
- Permaculture: This design principle emphasizes the harmonious integration of landscape and people, creating sustainable ecosystems.
- Organic Gardening: Avoiding synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, organic gardening promotes biodiversity and soil health.
- Animal Husbandry: Raising animals for food, wool, or companionship is a common practice. Ethical treatment and sustainable practices are key.
- Food Preservation: Canning, drying, and fermenting allow homesteaders to store food for longer periods, reducing waste and reliance on store-bought products.
These practices not only contribute to self-sufficiency but also foster a deeper connection with the environment and the food we consume.
The Benefits and Challenges of Homesteading
Homesteading offers numerous benefits, but it also comes with its own set of challenges. On the positive side, homesteaders often experience:
- Healthier Lifestyle: Consuming homegrown, organic produce can lead to better health outcomes.
- Environmental Impact: Reducing reliance on industrial agriculture and fossil fuels helps decrease one’s carbon footprint.
- Financial Savings: Over time, producing your own food and energy can lead to significant cost savings.
- Personal Satisfaction: The sense of accomplishment from creating a self-sufficient lifestyle is immensely rewarding.
However, homesteading also presents challenges, such as the initial investment in land and equipment, the need for a wide range of skills, and the time commitment required to maintain a homestead. Despite these hurdles, many find the lifestyle changes to be worthwhile and fulfilling.
Conclusion: Embracing the Homesteading Lifestyle
In conclusion, homesteading is a journey toward self-sufficiency and sustainable living. It requires dedication, hard work, and a willingness to learn new skills. However, the rewards of living a more environmentally friendly and self-reliant life are significant. As more people seek to reduce their impact on the planet, homesteading offers a viable and fulfilling path. Whether you’re considering a full transition to homesteading or simply incorporating some of its practices into your life, the benefits of this lifestyle are well worth exploring.